Hey, Screen Sultans! How are you all doing? We hope you are enjoying your long gaming sessions with full joy and excitement. But make sure to balance your screen time as well. So let’s not waste our precious reader’s time and jump to today’s topic of “What is Ray Tracing?” with no further delay.
Tada!! We’ll be discussing all about ray tracing and how it is used for different things and various related matters thereto. First of all, the question pops up in our minds: what exactly is ray tracing? It sounds like something related to light. Are we all thinking the same? Majorly yes! If you got us on this, then we share the same intellect as we share the same humor!
Ray Tracing refers to the technique that is used to stimulate the rays of light with how they interact with objects used in computer graphics as seen in the virtual world. However, it does trace the light path as the light bounces off from the surface and then interacts with different related materials. Meanwhile, it creates the respective shadows and reflections too. The practice of producing realistic pictures and images with the proper amount of light rays and shadows is said to be Ray Tracing. This method is mainly used in animation, Video gaming, and Visual industries. |
What will you see here?
Introduction to Ray Tracing
Talking about the ray tracing is a concept which is specifically used in computer graphics in the early 1960s. However, the researchers explored different ways to stimulate the behavior pattern of light in the virtual world. One of the significant mentions of ray tracing was found in “A Ray Tracing Algorithm for Progressive Radiosity” paper by Turner Whitted in the year 1968. Moreover, with the advancement in technology, there was a major development in ray racing techniques too.

The interesting thing about this feature was that it was known to the people when in 1986, the film named Young Sherlock Holmes was released. Here In this movie, fully computer-generated characters were created with the help of ray tracing. History was made and it was so PHOTOREALISTIC!
Jumping to the 1990s, ray tracing in commercial applications and software like POV-Ray (Persistence of Vision Raytracer) and Autodesk’s 3ds Max increased. It was used for offline animation and filmmaking. Thus there has been massive development in the Graphic Processing Units such as NVIDIA’s RTX technology which made real-time ray tracing efficient. In a way, Ray tracing is still evolving and reaching heights.
How Ray Tracing Works
The process of ray tracing is very simple yet complicated. It’s not that easy but it’s not that hard too. So we’ll simplify how these ray tracing tools work and this might be a useful aid for you. Let’s get started!
Ray Generation:
The first and foremost step starts with generating primary rays for each pixel presented on the screen. Then they originate from the camera and pass through the corresponding pixel lying on the image plane.
Intersection Point Testing:
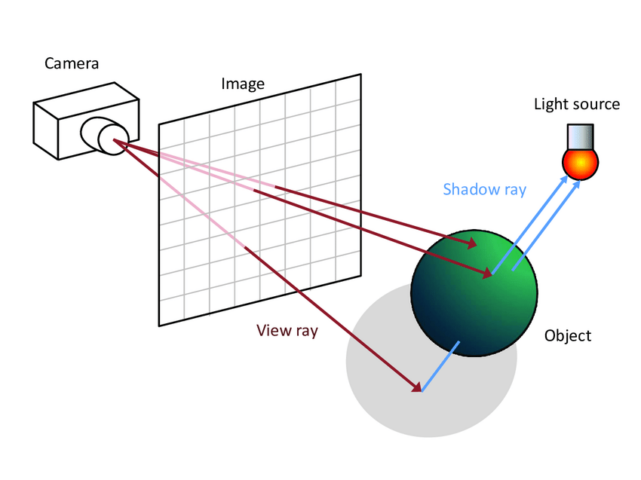
To determine whether the intersection is done for any objects or surfaces when the primary ray is traced into the scene. This is however possible by checking for the intersection in the scene with the help of geometry practice. For example, take any shape such as a triangle for an object and planes for surface angles.
Shading Calculation:
As soon you are done with the intersection point, there comes the time for Shading Calculation! This means calculating the color and the intensity of the light, by considering the material properties, light sources, and angle of incidence in the scene place.
Reflection and Refraction:

However additional rays are traced when the material at the intersection point is reflective or refractive. These rays are traced in the direction of the light that is reflected. While on the other side, the refraction rays are traced according to the laws of refraction.
Rays of shadow:
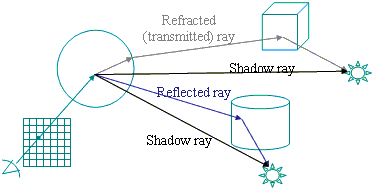
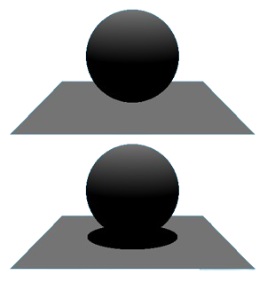
Shadow rays are traced from the point of intersection to each light source to determine a point in the shadow scene. Additionally, if any object intersects with the ray, the point in the shadow receives the low light.
Global Illumination:

For having a realistic lighting effect, these additional rays can be traced to stimulate the Global Illumination effects from the other objects present in the scene.
Circular Ray Tracing:
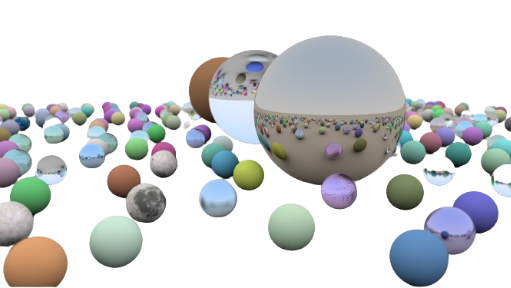
However, to stimulate the very complex transactions of the light, these rays can be recursively traced for refractions, reflections, and even other effects. But this method is expensive and is restricted to a certain number of bounces too.
Formation of the Image:
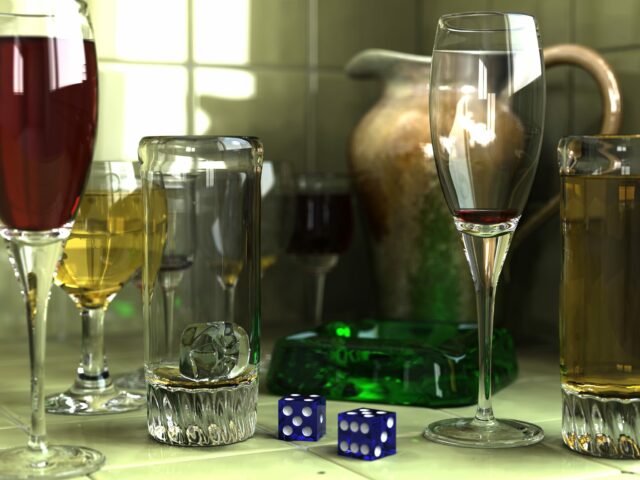
At last, you are at the last step which is the formation of an image. Here the color values calculated for each specific pixel are then combined to form the image to display it on screen.
Ray Tracing Techniques
So as we all know so far through this blog tracing works as the tracing of rays of light from the camera to the screen. This is where they interact with different objects. The rays get reflected, refracted, or absorbed based on the characteristics of the surface of the object. However, by tracing the multiple rays for the specific accounting and pixels for their interactions, these rays can create highly realistic pictures and images with accurate shadows and lighting.Â

Additionally, several techniques are used in ray tracing to enhance the process and to improve the quality of the final image so generated. Some of the most used techniques are the Ray object intersection test, simulating effects, and handling complex lighting scenes. Talking about the Hybrid rendering approaches specifically, this approach combines the strength of various rendering techniques. Named as Rasterization and Ray Tracing which is used to have a balance between the quality and performance.
Let us know more about some of the Hybrid rendering approaches below!

- Ray-Traced Effects with Rasterization: Under this technique, the geometry scene is rendered, and effects like reflections, shadows, and ambient occlusion are figured out using the ray tracing feature. This balances the visual fidelity and rendering speed for better performance.
- Screen space reflections (SSR): SSR uses the available information to simulate the reflections in the screen buffer. But it has got some limitations as well. Such as missing reflections outside the space screen or not properly visible surfaces.
- For shadows: One of the essential elements is a shadow in ray tracing as it plays a vital role in scene realism. Ray tracing can easily produce more accurate soft shadows as compared to the rasterization used for the approximation of shadows.
- Adaptive rendering: Talking about some of the hybrid approaches that switch between ray tracing and rasterization on the complex scene and viewpoint of the camera. Some examples of such practices are ray tracing used for reflections and rasterization used for other parts of the scene to maintain balance.
These hybrid rendering approaches are increasingly used in real-time applications, such as video games, where balancing rendering quality and performance is essential. Through the integration of many rendering algorithms, hybrid systems can attain amazing visual quality without sacrificing efficiency.
Applications of Ray Tracing
After exploring ray tracing working, various techniques, and its basic information, let us know more about the applications. These applications are used across various industries because they can create highly realistic images. Some of the most used applications are given below!

- Film and Animation Industries: To produce breathtaking visual effects and lifelike animations, ray tracing is commonly used in the film and other animation industries. But it also makes it possible to simulate realistic shadows, lighting, backgrounds, and character designs.
- Video Games and Interactive Media: Traditional output being computationally expensive for real-time rendering, ray tracing is used for the advancements in hardware and software to make it feasible for the gaming and interactive media industry. It also enhances the quality of visuals with realistic lighting and refractions.
- Architectural Visualization: It is also used to create realistic drawings and images of structures and interior spaces in architectural visualization. Architects can better organize their thoughts and see their plans with the aid of technology. By choosing materials and lighting with knowledge.
- Product Design and Marketing: Ray tracing is used in product design and marketing to create realistic renderings of products before they are physically manufactured. This helps designers develop their ideas and generate eye-catching beautiful marketing materials. Additionally, it also allows them to see how things will appear in various lighting and environment scenarios.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: As we already know ray tracing may provide more realistic lighting and reflections. So it can however improve the quality of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experiences. This may result in virtual worlds that are more realistic and entertaining to experience.
Benefits of Ray Tracing

We can easily predict that there are numerous benefits of ray tracing as we have already learned a lot from the above reading. But let us make it more informative for you. Some of the major benefits are explained here in below!
- Realistic and Improved Visual Quality: Ray tracing accurately calculates the light interaction with objects and improves the visual quality. It also enhances the overall appearance of the images and animations.
- Accurate Lighting Effects: These contribute to the rendered scene generation and simulate the complex lighting effects, caustics, and illumination with accuracy.
- Realistic Reflections: It can easily simulate the refractions and surface scenes. Such as glossy materials and mirrors irrespective of having rough or textured surfaces. It adds depth to the generated images.
- Consistency and Predictability: Produces the predictable and consistent results that are used by artists and designers. This becomes an efficient iteration and redefines the scenes by generating better overall results.
- Flexibility and Versatility: It is one the versatile techniques to generate various range of visual effects. However, it is also flexible enough to be suitable for various applications, gaming, film, and other visualization elements.
Summarising in short ray tracing’s ability to produce realistic lighting, shadows, reflections, and other visual effects makes it a significant tool for creating visually stunning digital content across various industries.
Challenges and Limitations

As a coin has two sides, it is very obvious that with advantages, there come challenges! Having numerous benefits, ray tracing has very few limitations. Let us discuss some of them to have respective solutions in the said case.
- Performance Considerations: Impacts the rendering times and frame rates as high-traced images require significant processing power and memory. So it becomes difficult for real-time applications like video games.
- Hardware Requirements: Heavy budget requirements as specialized software such as GPUs like NVIDIA’s RTX series are necessary. This however adds the cost to the system.
- Software Requirements: Various software are required to support ray tracing in terms of rendering content creation tools. Some of the major graphic APIs like DirectX and Vulkan include ray tracing support.
- Scene Complexity: Becomes challenging to render ray tracing in real-time as it uses complex lighting setups, intricate geometry, and various objects.
- Noise and Convergence: Produces noisy images while using path tracing techniques. It also relies on random sampling to simulate light paths.
Despite these few challenges, advancements in hardware and software, as well as optimizations in rendering algorithms, it continue to improve the feasibility and quality of ray tracing.
Frequently Asked Questions
| What is ray tracing acceleration? |
|---|
| Ray tracing acceleration is a technique for hardware optimization that speeds up the tracing process. Additionally, it is an intensive technique as it involves ray tracing through light and calculates the interaction between object and surface. As well as one of the common acceleration techniques is the use of data structures like bounding volume hierarchies (BVH). These brilliant BVHs organize objects in the scene into a hierarchy of bounding volumes. Such as bounding boxes or spheres. However, this hierarchy allows rays to quickly identify which objects they might intersect with, reducing the number of calculations needed. |
| What is Global Illumination in ray tracing? |
|---|
| Global illumination is the great simulation of indirect lighting in a scene. Though which includes the effects such as diffuse interreflection, specular reflection, and color bleeding. Moreover, it helps create more realistic lighting in ray-traced images. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, ray tracing is a cultured rendering technique that simulates the behavior of light to create realistic images in a computer graphical world. It also traces the path of light rays as they interact with objects in a scene. Which calculates the color and brightness of pixels to produce highly detailed and accurate images.
Ray tracing is used in various industries, including gaming, film, architecture, and design, to create visually stunning and alluring experiences. While computationally intensive, ray tracing is becoming more accessible with advancements in hardware and software. By leading to its increasing use in real-time applications. Overall, ray tracing represents a significant advancement in rendering technology, offering incomparable realistic and visual quality in digital images.
















