The process of monetizing your content might seem hard and confusing. Moreover, if you are going to spend some money on ads, it is better to spend it in the right place. Here is a guide to Google Ads for you to understand.
What you will see?
Google Ads

Google Ads is a powerful tool for businesses and individuals looking to advertise their products and services to a wider audience. It allows you to display ads on Google’s search engine results pages and other websites of the Google Display Network. One of the key features of Google Ads is its ability to target specific audiences. Advertisers can target audiences based on a variety of factors. This includes geographic location, interests, and search keywords. By targeting specific audiences, businesses can ensure that their ads are being shown to the people who are most likely to be interested.
Another important feature is its pay-per-click (PPC) model. With PPC, advertisers only pay when someone clicks on their ad. This makes it a cost-effective way to reach a wider audience. Advertisers can set a budget for their ads and bid on specific keywords or placements to compete for ad space. One of the most important factors in the success of a Google Ads campaign is the ad copy and visuals. Advertisers need to create compelling ads that will grab the attention of potential customers. Ad copy should be concise and to the point, highlighting the benefits of the product or service being advertised. Visuals should be eye-catching and relevant to the ad copy, helping to further grab the attention of potential customers.
Moreover, businesses can also use Google Ads to track their advertising success. Google Ads provides a wealth of data and analytics. Thus, allowing businesses to see how their ads are performing and make adjustments as needed. Advertisers can track metrics such as click-through rate, conversion rate, and cost per conversion, helping them to optimize their campaigns and maximize their return on investment.
Why advertise on Google?
Advertising on Google can provide businesses with a number of benefits that make it a worthwhile investment.
- Reach: Google is the most popular search engine in the world, with billions of searches conducted every day. By advertising on Google, businesses can reach a huge audience and increase their visibility to potential customers. Additionally, Google Ads allows businesses to display their ads on a variety of platforms.
- Targeting: Google Ads provides businesses with a range of targeting options that can help them reach their ideal audience. Advertisers can target audiences based on a variety of factors. This means that businesses can ensure that their ads are being shown to the people who are most likely to be interested.
- Cost-effective: Google Ads uses a pay-per-click (PPC) model, which means that businesses only pay when someone clicks on their ad. This way businesses can set a budget for their ads and only pay for the clicks they receive. Additionally, Google Ads provides a range of tools and analytics. This can help businesses optimize their campaigns and get the most for their money.
- Measurable results: Google Ads provides businesses with a wealth of data and analytics. This can be used to track the success of their campaigns and make adjustments as needed.
- Flexibility: Google Ads allows businesses to create a wide range of ad formats, including text, image, and video ads. Additionally, businesses can target specific devices and platforms. This allows them to create ads that are optimized for different types of users and devices.
Google Ads Best Practices
PPC Planner
PPC Planner is a tool within Google Ads that help advertisers plan their pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns. It provides insights and recommendations to help create effective campaigns that can maximize the return on investment. The PPC Planner tool uses machine learning to analyze historical campaign data and identify opportunities for improvement. It can recommend bid adjustments, suggest new targeting options, and provide insights into the potential impact of changes to a campaign. Advertisers can select a campaign and enter their advertising goals, such as increasing website traffic or driving more conversions. The tool will then analyze the campaign data and provide recommendations to help the advertiser achieve their goals.
No broad keyword terms
When creating a Google Ads campaign, it’s important to choose the right keywords to target. While broad keywords can seem like a good way to reach a wider audience, they can often be less effective than more specific, targeted keywords. These broad keyword terms are generally not a good idea because they tend to have high competition. This means that advertisers may end up paying more per click to have their ads shown. This can quickly affect your budget and result in lower ROI. Another issue with using broad keyword terms is that they are often less relevant to specific products or services. This can result in lower click-through rates (CTRs) and lower quality scores, which can negatively impact a campaign’s performance.
Additionally, broad keywords may generate more clicks. However, they are also more likely to attract users who are not actually interested in the products or services. This can lead to lower conversion rates and ultimately lower ROI. Moreover, using broad keyword terms can result in wasted spend. Because broad keywords can attract less relevant traffic, advertisers may end up wasting a significant portion of their advertising budget on clicks that don’t result in conversions. Instead, it’s generally better to use more specific, targeted keywords that are relevant to the advertiser’s products or services. This increases relevance, improves quality scores, increases conversion rates, and ultimately achieves better results and maximizes their advertising ROI.
Irrelevant ads
One of the challenges is ensuring that ads are relevant to the user’s search query. If an ad is not relevant to what the user is searching for, they are less likely to click on it. Thus, resulting in lower click-through rates (CTRs) and lower conversion rates. To help advertisers address this challenge, Google offers a feature called Responsive Search Ads. Responsive Search Ads allow advertisers to create multiple ad headlines and descriptions. Google then uses this to dynamically generate ads that are more relevant to the user’s search query.
Responsive Search Ads also allow advertisers to test different combinations of ad headlines and descriptions, and optimize their campaigns based on performance data. However, while this can be a powerful tool for improving ad relevance and performance, they are not a replacement for creating high-quality, relevant ad content. Advertisers still need to ensure that their ad content is well-written, clear, and relevant to the user’s search query.
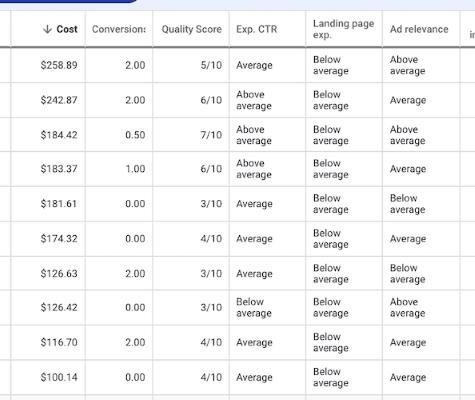
Improve Quality Score (QS)
The Quality Score (QS) is an important metric in Google Ads that measures the relevance and quality of your ads, keywords, and landing pages. A higher QS can lead to lower costs per click (CPC), higher ad rankings, and ultimately better ROI for your campaign. Ensure that the keywords you’re targeting in your ads are relevant to the content on your landing pages. This will help ensure that your ads are more closely related to the user’s search query, which can improve your QS. Optimize your landing pages to be easy to navigate, load quickly, and contain relevant content that is closely related to your ad copy and keywords. This will ensure that users have a good experience when they click on your ad, which can lead to higher QS.
Compelling ad copy can also help improve your QS. Write ads that include your targeted keywords and use language that is relevant to your target audience. Focus on the benefits of your product or service and use a clear call to action. Using ad extensions can provide additional information to users and make your ads more compelling. This can help improve your click-through rate (CTR), which is another important factor in determining your QS.
Optimize ad landing page
Optimizing your ad landing page is crucial for improving the performance of your Google Ads campaign. A landing page’s user experience can affect your ad’s visibility, click-through rate, and cost-per-click, so it’s important to make sure it provides a positive experience. To optimize your landing page, ensure that it is relevant to the ad the user clicked on. The content, visuals, and messaging on the landing page should align with the user’s search intent and the ad. Your landing page should also have a clear and visible call-to-action (CTA) that matches your ad’s CTA. Use language that motivates the user to take action, such as “Buy Now,” “Learn More,” or “Sign Up Today.”
A landing page’s loading speed is also important as it can impact the user’s experience. Ensure that your landing page loads quickly by optimizing its images, code, and hosting. It’s also essential to have a mobile-friendly landing page. This is because most users access the internet through their mobile devices. The landing page should be easy to navigate on smaller screens, load quickly, and have an optimized design.
Standard terms on Google Ads
When you are starting out knowing about terms that are commonly used while advertising is very important. This way you can set up, manage, and enhance your Google Ads more efficiently.
AdRank
AdRank determines the placement and visibility of your ads on the search engine results page (SERP). It is calculated based on the maximum cost-per-click (CPC) bid and Quality Score (QS) of your ad. The higher your AdRank, the more likely your ad will appear in a prominent position in the SERP. AdRank considers several factors, including the relevance and quality of your ad copy, landing page experience, expected click-through rate, ad format, ad extensions, and historical performance. To improve your AdRank, you can focus on improving your QS. To do this, optimize your ad copy, landing page, and ad targeting. Using relevant keywords and messaging, providing a positive user experience on your landing page, and testing and optimizing your ad copy can all contribute to a higher QS.
Bidding
Google Ads uses a bidding system to determine which ads appear on the search engine results page (SERP) and in what order. The bidding system is based on the concept of pay-per-click (PPC), where advertisers pay for each click on their ad. There are several types of bidding strategies available in Google Ads. This includes manual CPC, target CPA, target ROAS, and enhanced CPC. Manual CPC allows you to set a maximum CPC bid for each keyword. Target CPA and target ROAS allow you to set a target cost-per-acquisition or target return on ad spend, respectively. Enhanced CPC is an automated bidding strategy that adjusts your manual CPC bid based on the likelihood of a click leading to a conversion. The bidding system also considers other factors. This includes ad relevance, landing page experience, and expected click-through rate, when determining which ad to display and in what position.
The bidding system in Google Ads is a competitive auction, where advertisers bid against each other for ad placement. However, the highest bidder does not always win. Google also considers ad quality and relevance when determining ad placement. To optimize your bidding strategy, it’s essential to continuously monitor and adjust your bids based on performance data. You can use tools such as Google Ads’ bid simulator or automated bidding to help you make informed bidding decisions.
Campaign Type
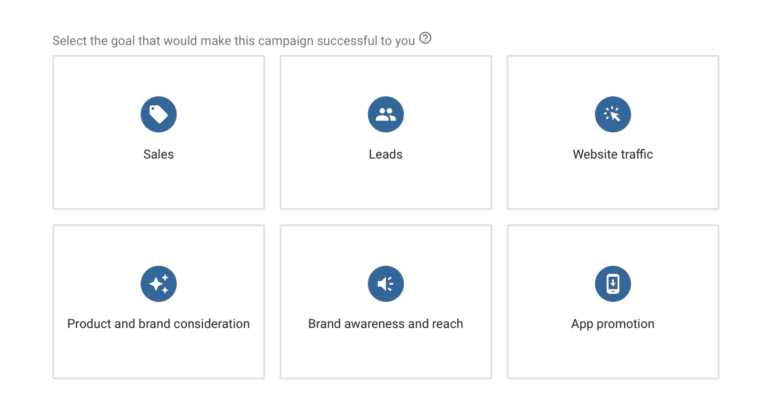
Google Ads offers several campaign types that advertisers can choose from based on their advertising goals and target audience.
- Search campaigns: These campaigns display text ads on the search engine results page (SERP) when users search for specific keywords. These are suitable for businesses looking to increase website traffic and generate leads.
- Display campaigns: These campaigns display banner ads on websites across the Google Display Network. These are suitable for businesses looking to increase brand awareness and reach a broader audience.
- Video campaigns: These campaigns display video ads on YouTube and across the Google Display Network. These are suitable for businesses looking to increase brand awareness and engagement.
- Shopping campaigns: These display product listing ads (PLAs) on the SERP when users search for products related to the advertiser’s offerings. These suit businesses that are looking to increase online sales and attract more qualified leads.
- App campaigns: These campaigns display ads across Google’s search, display, and video networks to promote mobile app installs and engagement. These are suitable for businesses looking to increase app installs and user engagement.
Each campaign type has its own set of features and targeting options. Advertisers can select the most appropriate campaign type based on their advertising goals, target audience, and budget. In addition to campaign types, Google Ads also offers campaign subtypes, such as standard, all features, and smart campaigns. These subtypes provide additional customization and automation options to help advertisers optimize their campaigns and achieve their advertising goals.
Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Click-Through Rate (CTR) is a metric used in Google Ads to measure the effectiveness of an ad campaign. It represents the percentage of users who clicked on an ad after seeing it. CTR is calculated by dividing the number of clicks an ad receives by the number of impressions it generates. A high CTR indicates that an ad is relevant and engaging to users. However, a low CTR may indicate that an ad is not resonating with the target audience. Advertisers can use CTR to evaluate and optimize their ad campaigns. Factors that can affect CTR include ad relevance, ad copy, targeting options, and the competition for keywords. Advertisers can improve CTR by creating relevant and engaging ad copy, targeting specific keywords and demographics, and using ad extensions to provide additional information and a call to action.
Conversion Rate (CVR)
Conversion Rate (CVR) measures the percentage of users who complete a desired action on a website after clicking on an ad. The desired action can be anything from making a purchase to filling out a contact form. CVR is calculated by dividing the number of conversions by the number of ad clicks. A high CVR indicates that an ad is effective in driving conversions. Whereas, a low CVR indicates that the landing page or the offer is not compelling enough. Factors that can affect CVR include the landing page design, the offer, the ad copy, and the targeting options.
Display Network
The Google Ads Display Network is a collection of websites, mobile apps, and other online platforms that allow advertisers to display their ads to a wider audience beyond the search engine results pages. The Display Network includes millions of websites, ranging from small blogs to large news sites and online marketplaces. This offers several targeting options, including demographics, interests, topics, and placements. Advertisers can also use remarketing to show ads to users who have previously interacted with their website or other online assets. Ads can be in various formats, including static images, animated GIFs, videos, and HTML5. Advertisers can use responsive ads to automatically adjust the ad format, size, and appearance to fit different placements and devices.
The Display Network can be an effective way to reach a wider audience and increase brand awareness. It can also be used to drive website traffic, promote products or services, and generate leads or sales. Moreover, advertisers should create visually appealing ads that align with their brand identity and messaging. They should also use targeting options that are relevant to their target audience. Moreover, they need to regularly monitor and optimize the campaigns to improve performance.
Extensions
Ad extensions are additional pieces of information that can be added to Google Ads text ads to provide more context and increase the visibility and relevance of the ads. This includes clickable links, additional text, phone numbers, locations, reviews, and more. Google Ads offers several types of ad extensions,. This includes site link extensions, callout extensions, structured snippet extensions, call extensions, message extensions, location extensions, and more. Advertisers can choose which ad extensions to use based on their goals and target audience. Ad extensions can help improve ad performance by increasing the ad’s visibility. Thus, providing additional information to users, and making the ad more relevant to their search intent. It can also help increase the ad’s click-through rate, conversion rate, and overall quality score.
Keywords
Keywords are words or phrases that are used to match a user’s search query with an advertiser’s ad. Advertisers can choose which keywords to target based on their products or services. Google Ads offers several keyword matching options, including broad match, phrase match, exact match, and broad match modifier. These options allow advertisers to control how closely a user’s search query must match their chosen keywords for their ad to be triggered.
Choosing the right keywords can help advertisers reach their target audience. This increases ad relevance and improves their click-through rate and conversion rate. On the other hand, targeting irrelevant or highly competitive keywords can lead to wasted ad spend and poor campaign performance. Advertisers should conduct thorough keyword research to identify the most relevant and profitable keywords for their business. They should also regularly monitor and optimize their keyword targeting to improve their ad performance and achieve their advertising goals.
PPC
PPC, or pay-per-click, is a type of online advertising model that allows advertisers to pay for each click on their ads. Advertisers choose the maximum bid amount they are willing to pay for each click on their ad. Then, Google uses an auction system to determine which ads are displayed on the SERP and in what order. PPC advertising gives the ability to target specific keywords and search terms, reach a wide audience, and track ad performance and return on investment (ROI) in real time. Advertisers can also use advanced targeting options. This includes location targeting, device targeting, and audience targeting, to reach their ideal target audience.
To make the most of PPC advertising on Google Ads, advertisers should conduct thorough keyword research, create relevant and compelling ads, and regularly monitor and optimize their ad performance to improve their click-through rate, conversion rate, and overall ROI.
Quality Score (QS)
Quality Score is calculated based on several factors. This includes the relevance and quality of the ad text, the relevance and quality of the landing page, and the click-through rate (CTR) of the ad and its corresponding keywords. A high QS can lead to lower ad costs, higher ad rankings, and improved ad visibility. Advertisers can improve their QS by creating relevant and compelling ad text, targeting relevant keywords, and optimizing their landing pages to provide a good user experience. Quality Score is a dynamic metric that is recalculated each time an ad is eligible to be displayed on the search engine results page. Advertisers can monitor their QS in their Google Ads account and use it as a guide to optimizing their ad campaigns.
How does Google Ads work?
Google Ads allows businesses and advertisers to display their ads to potential customers across Google’s search engine results pages and display network. The platform works on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, where advertisers pay only when someone clicks on their ad. To use Google Ads, advertisers first create an account and set up a campaign. Within each campaign, advertisers create one or more ad groups, which contain a set of ads and the keywords that trigger those ads to appear. Advertisers can also choose to target specific geographic locations, devices, and audience demographics. Once the campaign is set up, advertisers bid on the keywords they want their ads to appear for. The bid amount represents the maximum amount the advertiser is willing to pay for a click on their ad.
Google uses an auction system to determine which ads appear on the search engine results page and in what order, taking into account factors such as the ad’s relevance, quality, and bid amount. When someone searches for a keyword or phrase that matches the advertiser’s target keywords, Google’s algorithm determines which ads to display based on the auction results. If the ad is clicked, the advertiser is charged the amount of their bid for that click. Google Ads offers a range of ad formats, including text ads, image ads, video ads, and shopping ads. Advertisers can also use ad extensions to provide additional information, such as a phone number or location, within their ads. Advertisers get a wide range of tools and metrics to help them monitor and optimize their campaigns, including conversion tracking, audience targeting, and ad performance reports.
Location
Advertisers can choose to target their ads to specific geographic locations, such as countries, regions, cities, or even specific zip codes. This is important because different regions may have different market demands, preferences, and purchasing behaviors. Location targeting can be set up at the campaign level, ad group level, or even at the individual ad level. Advertisers can also choose to exclude certain locations where they do not want their ads to appear. This is useful for businesses that only operate in certain regions or do not have the capacity to serve customers in certain areas.
When a user performs a search on Google, the search engine uses the user’s location to determine which ads to display. Location targeting can also be combined with other targeting options, such as language, device type, and audience demographics, to create more precise targeting strategies. However, this can also affect ad costs and performance. Advertisers may find that bids for certain locations are more competitive or have higher conversion rates than others. By monitoring the performance of their ads by location, advertisers can adjust their bidding strategies and targeting to maximize their return on investment.
Match Types
Match types determine how closely a search query must match a keyword in order for an ad to be triggered. There are several different match types available in Google Ads:
- Broad Match: This is the default match type and the most inclusive. Ads will show for searches that contain any words in the keyword, in any order, and with additional words. While this can provide a wide reach, it may also result in irrelevant clicks and lower conversion rates.
- Modified Broad Match: This is a variation of broad match that allows advertisers to specify certain words that must be included in the search query for the ad to appear. This is done by adding a “+” sign in front of the keyword. This can provide a balance between reach and relevance.
- Phrase Match: This match type allows ads to show for searches that include the keyword phrase in the same order, with additional words before or after the phrase. This can provide a more specific targeting than a broad match but still has some flexibility.
- Exact Match: This match type allows ads to show for searches that are an exact match to the keyword, without any additional words. This can provide the highest level of relevance and targeting but may have a limited reach.
Choosing the right match type for a keyword is important for achieving the desired level of targeting and reach. Advertisers can use a combination of match types for their keywords to provide a balance between relevance and reach. They can also use negative keywords to exclude irrelevant searches from triggering their ads.
Description and Headline
The headline and description are elements that grab a user’s attention and provide them with the most relevant information about the product or service being advertised. The headline is the first and most prominent piece of text in an ad. It appears at the top of the ad and is limited to 30 characters. A well-written headline should be attention-grabbing, concise, and clearly communicate the main benefit or selling point of the product or service being advertised. A strong headline can increase the click-through rate (CTR) of an ad, which can lead to more traffic and conversions.
The description is the supporting text that appears underneath the headline in a Google Ads ad. There are two description lines available, each limited to 90 characters. The description provides additional information about the product or service and helps to convince users to click on the ad. A well-written description should highlight the unique selling points of the product or service and provide a clear call-to-action (CTA) for users to take action. When creating Google Ads ads, it’s important to focus on crafting strong headlines and descriptions that will capture the user’s attention and compel them to click on the ad.
Google Ads Retargeting
Google Ads retargeting, also known as remarketing, is a strategy that allows advertisers to show targeted ads to users who have already interacted with their website or mobile app. This can include users who have visited specific pages on the site, added items to their cart, or completed a certain action. The idea behind retargeting is to bring users back to the website or app and encourage them to complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a lead form. By targeting users who have already shown an interest in the product or service, retargeting ads can be more effective than generic display ads.
There are several ways to implement retargeting on Google Ads. You can use a remarketing tag or pixel, which is a piece of code that tracks user activity on the website and allows advertisers to create retargeting audiences based on specific actions. Another option is to use Google Analytics to create retargeting audiences based on user behavior, such as time spent on the site or specific pages visited. Once a retargeting audience has been created, advertisers can create custom ads that are tailored to the user’s previous interactions with the site.
Types of Campaigns
Search Ads
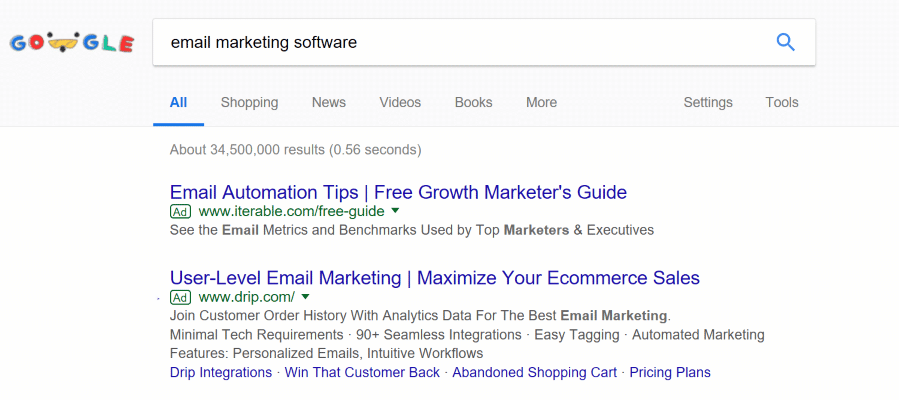
Search ads appear at the top or bottom of search engine results pages (SERPs) when a user searches for a specific keyword or phrase. They are highly targeted, as advertisers can select the specific keywords they want to target and create ad copy that is relevant to those keywords. Advertisers can also set a bid amount for each keyword. This determines how much they are willing to pay for each click on their ad. Search ads can be highly effective for driving traffic to a website or landing page. This is because users who click on the ad are typically actively searching for information related to the product or service. Advertisers can also track the performance of their search ads using Google Ads’ reporting and analytics tools.
To create a search ad, advertisers typically start by selecting the keywords they want to target and creating ad copy that is relevant to those keywords. Advertisers can also set a bid amount for each keyword. This determines how much they are willing to pay for each click on their ad. Once the ad is created, it will be reviewed by Google to ensure that it complies with the platform’s policies on ad content and landing pages. Once approved, the ad will be eligible to appear on relevant search engine results pages (SERPs) for the targeted keywords.
Responsive Search Ads (RSA)
Responsive Search Ads (RSAs) let advertisers create flexible and personalized ad copy. With RSAs, advertisers can create multiple headlines and descriptions that Google dynamically assembles to create the most relevant ad for each user. Machine learning algorithms optimize ad copy based on factors such as search query, device type, and user behavior. Advertisers can create up to 15 headlines and four descriptions per ad, and Google tests different combinations to determine the best-performing ones. RSAs can increase an ad campaign’s reach, creating a larger number of unique ad combinations than traditional search ads. They can also save time for advertisers, who do not have to create and test multiple ad variations manually.
Display Ads
Display ads are shown on websites, apps, and videos across the Google Display Network. They can be images, animations, or videos, and are designed to attract users’ attention and generate clicks or conversions. Display ads can help increase brand awareness, as they reach a large number of people across various platforms. Advertisers can target specific audiences based on factors such as demographics, interests, and behaviors. This allows for more effective ad delivery and increases the chances of converting users into customers. Ad creatives for display ads should be visually appealing and relevant to the target audience. Advertisers should consider using images or videos that showcase their products or services and include a clear call to action to encourage clicks.
Video Ads
Video ads allow advertisers to reach their target audience through engaging and interactive video content. They can be shown on YouTube and across the Google Display Network, allowing advertisers to reach a wide range of viewers on various platforms. These can help businesses increase brand awareness, communicate their message effectively, and drive conversions. Advertisers can use a variety of video formats, including skippable, non-skippable, bumper, and discovery ads. Each format has its own unique features and can be used to achieve different advertising goals.
Skippable video ads are the most commonly used format, and viewers can choose to skip the ad after five seconds. Non-skippable ads must be watched in their entirety before the viewer can continue to their desired content. Bumper ads are short and non-skippable, lasting only six seconds, and are ideal for increasing brand awareness. Discovery ads appear in search results and are designed to lead viewers to a video or landing page.
Google App Ads

Google App Ads allow advertisers to promote their mobile app to a relevant audience. App ads can be displayed on Google Search, Google Play, YouTube, and the Google Display Network. The primary objective of Google App Ads is to drive app installs and engagements. Advertisers can use different ad formats, including app installs, app engagement, and app discovery ads, to reach their target audience effectively. App install ads are designed to drive app downloads and can be displayed on Google Play, search results, and the Display Network. These are used to drive users to engage with the app and can be displayed on Google search and YouTube.
Shopping Ads
Another type of Google Ad is a campaign for Google Shopping. Like other types of advertisements, shopping campaigns are displayed on SERPs and incorporate particular product information like the item’s price and picture. You can start a campaign for online shopping through Google Merchant Center, where you offer specific product data that Google utilizes to create your shopping ads. Advertising certain products and product categories, as opposed to your company as a whole, is possible with shopping ads. As a result, when you use Google to search for a particular product, adverts for several companies appear at the page’s top and/or side.
Using Google Ads Easily
The first step is to create a Google Ads account. Sign up for a Google Ads account and follow the setup process to create your account. Once you’ve created your account, define your advertising goals. Decide what you want to achieve with your advertising campaign, whether it’s increasing brand awareness, generating leads, or driving sales. Next, choose your campaign type. Select the campaign type that aligns with your advertising goals. Within your campaign, create ad groups that target specific audiences and keywords. This will help ensure your ads are displayed to the right people. After creating your ad groups, it’s time to create your ads. Add headlines, descriptions, images, and calls to action that will entice potential customers to click on your ads. Ensure your ads are relevant to your target audience and reflect your advertising goals.
Link Google Analytics
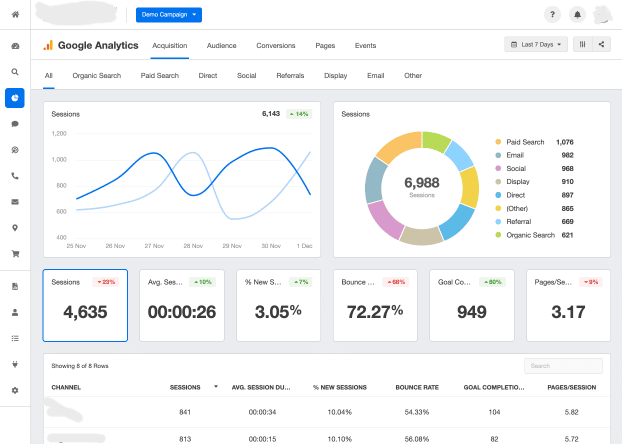
Linking Google Analytics to your Google Ads account allows you to track and analyze user behavior on your website. You gain deeper insights into the performance of your Google Ads campaigns. Moreover, you can optimize your advertising strategy to better reach your target audience. Once your accounts are linked, you can access a wealth of information about user behavior on your website directly within your Google Ads account. You can view metrics such as bounce rate, time on site, and conversion rate. This can help you make informed decisions about your ad targeting and optimization. Furthermore, you get the ability to create remarketing lists based on user behavior.
Add UTM codes
Adding UTM codes to your Google Ads campaigns helps you to track the performance of your ads. UTM codes are parameters that are added to the end of the URL of your ad’s landing page. These codes allow you to track the source, medium, and campaign name of the traffic that your ad is generating. By adding UTM codes, you can easily track the effectiveness of your ads and make data-driven decisions to optimize your campaigns. To create UTM codes, you can use Google’s Campaign URL Builder tool. This tool allows you to enter the URL of your landing page and add the UTM parameters that you want to track. You can add parameters such as the source, medium, campaign, term, and content. After that, you can generate a unique URL with the UTM codes included.
You can track the performance of your ads in Google Analytics. There you can view the traffic that your ads are generating and the behavior of the users that are clicking on your ads. You can see metrics such as the number of clicks, impressions, click-through rate (CTR), and conversion rate.
Set up conversion tracking
Conversion tracking allows advertisers to measure the effectiveness of their campaigns and optimize them accordingly. Advertisers can track and analyze the actions taken by their website visitors, such as making a purchase, filling out a form, or subscribing to a newsletter. Once conversion tracking is set up, advertisers can view the data in their Google Ads account and use it to optimize their campaigns for better performance. They can track conversion rate, cost per conversion, and conversion value to understand how their campaigns are performing and make data-driven decisions to improve them.
Integrate your Google Ads with your CRM
Integrating your Google Ads account with your CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system can provide valuable insights and help you make informed decisions about your advertising strategies. By linking these two platforms, you can track the performance of your ad campaigns and identify which ones are driving the most leads, conversions, and revenue. To set up, you first need to ensure that your CRM system is compatible with Google Ads. After integration, you can see which ads are driving the most valuable conversions, gain insights into your customer’s behavior, and optimize your ad campaigns accordingly. Additionally, you can use the data collected from your CRM to create highly targeted remarketing campaigns. This will help in effectively reaching users who have shown interest in your product or service.
Bidding Strategies
It’s time to start bidding once your ad campaigns are set up and tracking is established. Keep in mind that your potential to rank in Google Ads depends on your bid strategy. When starting your paid campaign, you should be aware of a few methods and bid settings, even though your bid amount will rely on your budget and objectives.
Automated vs Manual Bidding
With Manual Bidding, advertisers manually set bids for each keyword and placement in their campaigns. This provides full control over bid amounts but requires constant monitoring and adjustment to ensure optimal performance. On the other hand, Automated Bidding uses machine learning algorithms to adjust bids based on data such as conversion rate, cost per click, and other metrics. This method can save time and effort while potentially improving campaign performance. The best choice may depend on factors such as the advertiser’s experience and available resources, as well as the specific goals and performance metrics of the campaign. Some advertisers may even prefer to use a combination of both methods. Ultimately, the key is to continually evaluate and optimize bidding strategies to achieve the best possible results.
Bidding on Branded Search Terms
Bidding on branded search terms involves placing ads for keywords that contain the name of your brand or company. This can help you maintain top search engine rankings for your brand and drive more targeted traffic to your website. Advertisers can use various targeting options such as exact match, broad match, and phrase match to ensure that their ads appear only for relevant searches. It’s important to closely monitor the performance of these ads to ensure that they are driving conversions. The advantage is that it allows advertisers to control the brand’s online reputation by pushing down negative search results and highlighting positive ones. Additionally, by bidding on their own branded terms, advertisers can often achieve higher ad positions and lower cost-per-clicks (CPCs) than their competitors.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to bidding on branded terms. It may increase costs for keywords that would otherwise have low competition and CPCs. It can also lead to ad fatigue for users who frequently search for the same brand, causing them to ignore or block the ads.
Cost Per Acquisition (CPA)
Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) measures the cost of acquiring a conversion, such as a purchase or lead, through your ad campaign. This metric is essential in determining the profitability of your campaign and the return on investment (ROI) you are generating. CPA is calculated by dividing the total cost of your ad campaign by the number of conversions you have received. To optimize your campaign’s CPA, it is essential to focus on improving your conversion rate, reducing your cost per click (CPC), and increasing your click-through rate (CTR). This can be achieved through various tactics, such as improving your ad copy, targeting relevant keywords, and optimizing your landing page.
Using automated bidding strategies, such as Target CPA or Target ROAS, can also help to optimize your CPA by automatically adjusting your bids based on historical performance data and predicted outcomes. These strategies can help to balance the cost of acquiring a conversion with the value of that conversion to your business.
Conclusion
Given its power and reach, Google Ads will help you through your paid campaign. Even though some campaigns require a little bit more work, all Google Ads campaigns work amazingly. You get everything you need for an effective Google Ad campaign that generates clicks and leads. It has an easy-to-use pay-per-click platform. This allows you to set a budget that you don’t want to risk going over. Moreover, you can then see the analytics directly. Google ads will help you in promoting your company’s products and services at low prices. The reach and efficiency are much higher than its competitors available in the market. Also, Google Ads’ support will help you resolve ad-related issues.
Are you ready to monetize your content? If you have any doubts, you can ask in the comments section below.
















